India–Size and Location: CBSE Class 9 NCERT Geography: India is one of the ancient civilizations of the world and has a strategic location with lofty mountains in the north to a great peninsula in the south. The chapter India–Size and Location explains the coordinates of location of India, its size in the world, east-west and north-south extension, the prime-time meridian of India, India and the world, India’s neighbours and some other topics. Class 9 Geography Notes of the chapter ‘Location and Size of India’ are given here with proper classification under suitable headings. The Notes in Pdf can are also available for download. Link is given at the end of the notes.
Click here for such Class 9 geography study materials
Location and Size of India Class 9 Chapter Notes
Location
- India lies almost entirely in the Northern hemisphere.
- It lies in the southern part of Asia.
- India is referred to as the Indian subcontinent as it possesses all geographical features found in a continent.
- Indian mainland extends between latitudes 8°’4’N and 37°’6’N and longitudes 68°’7’E and 97°25’E.
- The Tropic of Cancer 23° ’30’N splits India into two almost equal parts.
- The north-south extent is about 3,214 kms while the east-west extent is about 2,933 Kilometres.
- Indira Point is the southernmost point of the Indian Union. It was submerged during the 2004 Tsunami. Kanyakumari is the southernmost tip of the Indian mainland.
- Indira Col in Ladakh is India’s northernmost point.
Size

- With an area of about 3.28 million square kms, India is the seventh largest country in the world.
- Despite having only 2.4% of the world’s total geographical area, India is the second most populated country in the world.
- India has a land boundary of about 15,200 kms.
- India has a long coastline of about 7,516.6 kms, including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands.
- India is surrounded by mountains in the northwest, north, and northeast.
- Down south, India is surrounded by three water bodies the Arabian Sea, the Indian Ocean, and the Bay of Bengal. Therefore, it is referred to as a peninsula.
- Due to the vast latitudinal and longitudinal extent, there is a time gap of two hours between the easternmost and the westernmost states Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat.
Standard Meridian & time lag
- The Standard Meridian of India (82°30’E) passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh and is considered as the standard time for India.
- The latitudinal extent tends to influence the duration of day and night. So, Kanyakumari being close to the equator, does not experience much difference in day and night. However, as we move northwards, the difference tends to increase. Therefore, Kashmir, which is about 30° away from the equator, experiences a more significant difference.
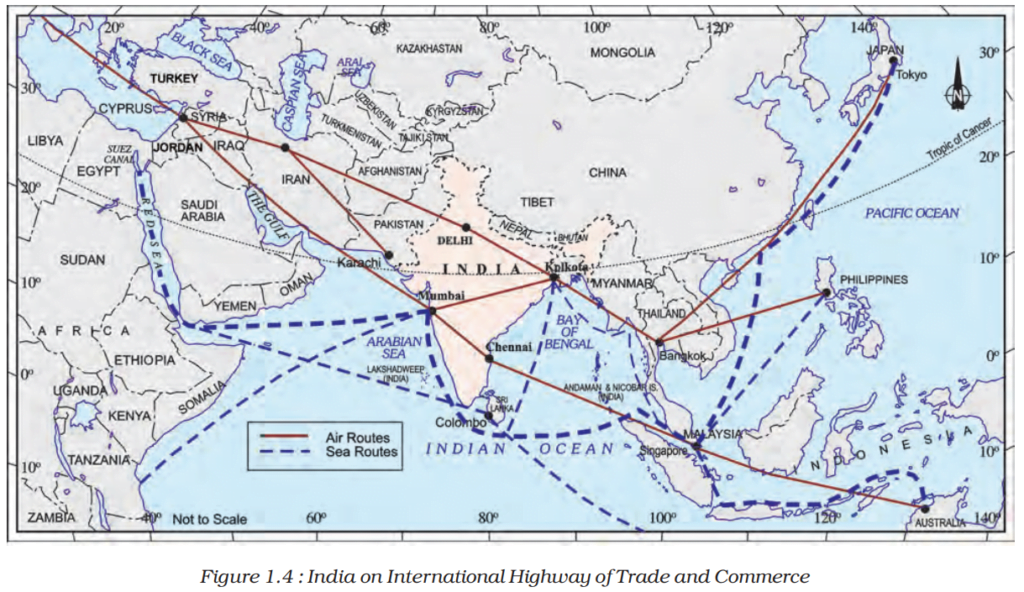
India’s Strategic Location in the world?

- The Indian landmass is located in the southern parts of Asia, with Deccan Peninsula protruding into the Indian ocean.
- Due to its strategic location and long coastline, India has been the centre of the trans-oceanic Indian Ocean trade. Therefore, the Indian Ocean has been rightly named after India.
- Lying at the head of the Indian Ocean, its maritime relations with countries of Europe, Africa, and West Asia in the west and Southeast Asia and East Asia in the east.
Role of Land Routes
- The Himalayan mountains bound India in its north, northwest, and northeast, and the passes have facilitated the exchange of ideas and merchandises between India and the world since time immemorial.
- Land routes like the Silk Route which connected East Asia to Rome in ancient times travelled by India. Besides, trade, these routes facilitated the exchange of religious ideas, traditions, arts and crafts.
- The philosophies of the Upanishads the Ramayana, the stories of Panchatantra, the Indian numerals, and the decimal system reached the rest of the world through the land routes used extensively by scholars.
- Even Indian culture was influenced due to these cultural exchanges that we can even see in different parts of the country. Most evident is the influence of Greek sculptural art form and the introduction of West Asian architectural styles in construction activities like domes and minarets.
India and her Neighbours
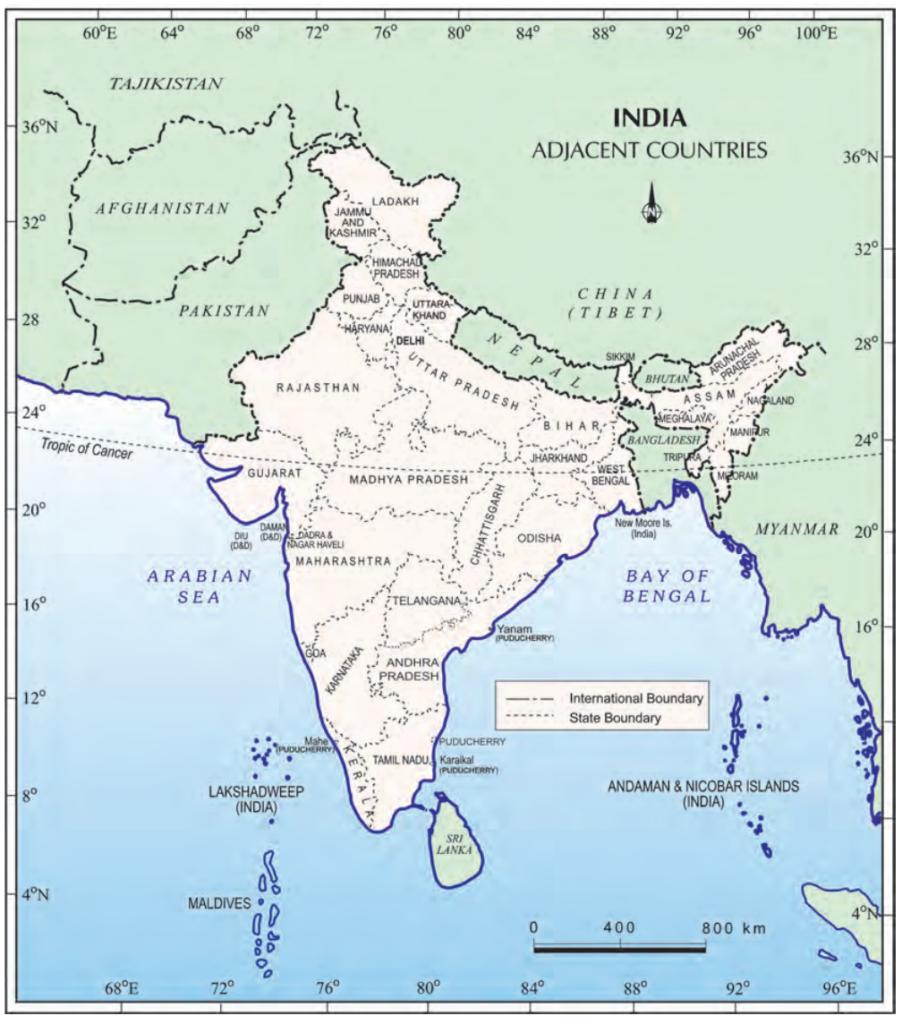
- India has 28 states and 8 union territories.
- Rajasthan is the largest state, while Goa is the smallest state
- Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, and Jharkhand do have an international border and are landlocked states
- Afghanistan and Pakistan in the northwest
- China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north
- Bangladesh and Myanmar in the east
- Sri Lanka and Maldives in the south. The water bodies Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar separate Sri Lanka from India.
- The Maldives lies in the Arabian Sea, south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
Indian states international frontiers
- Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat share their borders with Pakistan.
- Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh share their border with China.
- West Bengal, Mizoram, Assam, Meghalaya, and Tripura share their borders with Bangladesh.
- Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim share their borders with Nepal.
- Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram share their borders with Myanmar.
Click here for more such Class 9 geography study materials


