Overview of the chapter
- Different generations of computers
- First Generation: 1946-1958 (Vacuum Tubes)
- Second generation: 1959-1964 (Transistors)
- Third generation: 1965-1970 (Integrated Circuits IC)
- Fourth generation: 1971- today (Microprocessors)
- Categories of computers
- On the basis of working principle
- On the basis of size
- On the basis of brand
Introduction
- Computer are such an integral part of our everyday life.
- Computer is an electronic machine which performs mathematics and logical calculations.
- Charles Babbage is called the Father of computer.
- Now, in this chapter, we are trying to describe the types of computers and elaborate classification of computer.
- Computers can be classified in various ways depending on their generation, working, size and use.
Generations of Computer
- The term ‘Generations’ means improvement in the development of a product (computer).
- Every new generation, the circuitry has gotten smaller and more advances than the previous generation.
- New discoveries are constantly being developed that effect the way of we live, work and play.
The first generation: 1946- 1958 (Vacuum Tubes)

- The Ist generation computers were huge, slow, expansive and often unreliable.
- In 1946 two Americans, Presper Eckert and John Mauchly built the ENIAC.
- ENIAC was made up of 18,000 vacuum tubes and occupied a 30 * 50 feet room.
- ENIAC stands for Electronic Numeric Integration and Calculator.
Key Features
- Vacuum tubes based, punched tape input or output, about 1,000 circuits per cubic foot.
Examples- ENIAC, IBM models 604,650(drum memory), 701,702,704,705,709 etc.
| Things to remember: ENIAC was the world’s Ist successful electronic computer. |
The Second generation: 1959-1964 (Transistors)

- As the development moved further, the second generation computer knocked the door.
- In 1947, three scientists, John Bardeen William Shockley and Walter Brattain working at AT & T’s Bell Labs invented transistor.
- It was faster, more reliable, smaller & much cheaper to build than a vacuum.
- One transistor replaced the equivalents of 40 vacuum tubes.
- The size of computer also decreased and it became much smaller than that of earlier computer.
- Therefore, they were very cheap to produce.
Key Features
- Low electricity consumption.
- Mare reliable and faster.
- Used transistors, about 1,00,000 circuits per foot.
Examples – UNIVAC – III, IBM 7070, 7080,7090,1400,1600 series etc…
Third generation: 1965-1970 (Integrated Circuits IC)
- Invented in the year 1965.
- In this generation of computer, IC (Integrated Circuits) was used as the electronic component for computers.
- The development of IC gave birth to a new felid of microelectronics.
- It is small in size, superior performance and reliability than the previous circuits.
- Robert Noyce of Fairchild Corporation & Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments discovered the integrated circuits.
Key Features
- Low power consumption.
- Large scale IC, 10 million circuits per square foot.
Examples – IBM 360 series, GE 235 etc…
The Fourth generation: 1971- today (Microprocessors)

- This is the generation where we are working today. The computers which we see around us belong to the fourth generation computers.
- By putting millions of transistors onto one single chip more calculation and faster speeds could be reaches by computers.
- Ted Hoff, employed by Intel invented a chip.
- The size of a pencil eraser that could so all the computing and logic of a computer.
- It is evident that he next generation of computer i.e. fifth generation will be developed soon.
- In that generation, computer will possess artificial intelligence and it would be able to take self-decisions like a human beings.
Key Features
- Very large scale integration billions of circuits per cubic foot.
- Portable computer developed.
| Things to remember: Supercomputers can execute a single program faster than a mainframe. |
Examples– IBM system 3090, HP 9,000 etc…
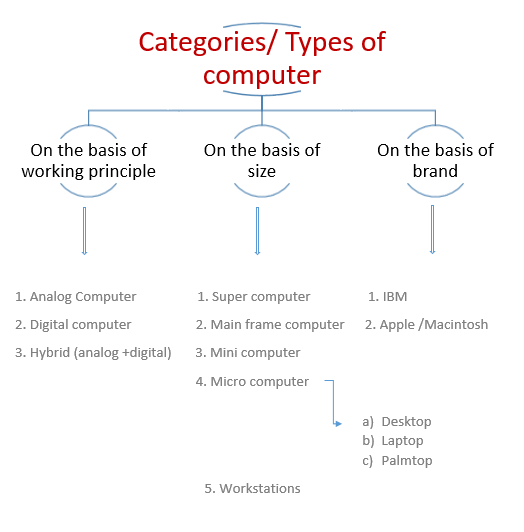
Analog computer
An analog computer is a computer that represents data by measurable quantities, as voltages than by expressing the data as numbers.
Example- Thermometer, speedometer, petrol pump indicator, multimeter etc.

Digital computer
A digital computer is the most commonly used type of computer and is used to process information with quantities using digits, usually using the binary number system.

Hybrid (analog + digital) computer
A combination of computers those are capable of inputting and outputting in both digital and analog signals. A hybrid computer system setup offers a cost effective method of performing complex simulations.

On the basis of size
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer that performs at or near the currently highest operational rate for computers.
It is mainly used for scientific and engineering applications that must handle very large databases or do a great amount of computation.
For example, weather forecasting requires a supercomputer.

Mainframe computer
It is very large and expensive computer capable of supporting 100 or even 1,000 of users at a time.
Mini computer
A computer with processing and storage capabilities smaller than those of mainframe but larger than those microcomputer.
On the basis of Brand
IBM computers
It refers to a family of personal computers by IBM.
Apple/Macintosh computer
It is also known a Mac, is a line of personal computers (PC’s) designed, developed, and marketed by Apple Inc.
Let Us Summaries
- Charles Babbage is called the ‘Father of computer’.
- The first generation computer were huge, slow, expensive and often undependable.
- One transistor replaced the equivalent of 40 vacuum tube.
- Integrated circuit were used as the electronic component for computer.
- The microprocessor led toward the invention of personal computer or microcomputers.
- Digital computer processes information with quantities using digit usually using the binary number system.
- Hybrid computer is a combination of computer those are capable of inputting and outputting in both digital and analog signals.
- Supercomputer perform at or near the currently highest operational rate for computers.
- A minicomputer is a multiprocessing system capable of supporting from 4 to about 200 users simultaneously.
- Desktop Computer is personal or micro-mini computer sufficient to fit on a desk.
- Laptop is a portable computer complete with an integrated screen and keyboard.
- Palmtops have no keyboard but the screen serves both as an input and output device.



I am so happy because It is very helpful,
THANKS
I am so happy😊 it is very helpful