India-Size and Location Class 9 Solutions: The chapter 1 of Clas 9 Geography explains India in terms of its size and location. India is a vast country ranking 7th in the world geography by size with 2.4% of the world geographical area. India accounts for 17% of the world population. Here you will find the solutions to the Chapter 1 of Geography Class 9.
India-Size and Location: NCERT Geography Class 9 Solution
Page No: 2
Find Out
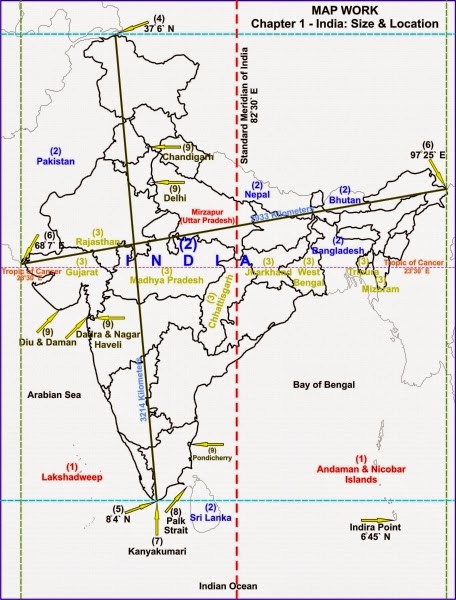
1. Why 82°30’E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India?
Answer
82°30′ E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India because it is situated in the centre of all longitudes and latitudes in which our country is located.
2. Why is the difference between the durations of day and night hardly felt at Kanyakumari but not so in Kashmir?
Answer The difference between the durations of day and night hardly felt at Kanyakumari because it is near equator. As equator receives the direct Sun rays, there won’t be hardly any difference between the day & night. But the Kashmir is far away from the equator.
Page No: 4
1. The number of Union Territories along the western and eastern coasts.
Answer
Union Territories on the western coast of India are — Diu and Daman, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Mahe (Pondicherry) and Lakshadweep.
Union Territories on the eastern coast of India are — Pondicherry and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
2. Area-wise which is the smallest and which is the largest state?
Answer
Largest Sate: Rajasthan Smallest State: Goa
3. The states which do not have an international border or lie on the coast.
Answer
Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Telangana.
4. Classify the states into four groups each having common frontiers with
(i) Pakistan
(ii) China
(iii) Myanmar and
(iv) Bangladesh.
Answer
(i) States having common frontiers with Pakistan are Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat.
(ii) States having common frontiers with China are Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
(iii) States having common frontiers with Myanmar are Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram.
(iv) States having common frontiers with Bangladesh are Meghalaya, Assam. West Bengal, Tripura.
Page No: 6
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
(i) The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through:
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Chhattisgarh
(c) Odisha
(d) Tripura
Ans. (c) Odisha
2. The eastern-most longitude of India is:
(a) 97°25′E
(b) 68°7′E
(c) 77°6′E (
d) 82°32′E
Ans. (a) 97°25′E
3. Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim have common frontiers with:
(a) China
(b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal
(d) Myanmar
Ans. (c) Nepal
4. If you intend to visit the island Kavaratti during your summer vacations, which one of the following Union Territory of India you will be going to?
(a) Pondicherry
(b) Lakshadweep
(c) Andaman and Nicobar
(d) Diu and Daman
Ans. Lakshadweep
5. My friend hails from a country which does not share land boundary with India. Identify the country.
(a) Bhutan
(b) Tajikistan
(c) Myanmar
(d) Nepal
Ans. (b) Tajikistan
2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea.
(ii) Name the countries which are larger than India.
(iii) Which island group of India lies to its south-east?
(iv) Which island countries are our southern neighbours?
Answer
(i) Lakshadweep
(ii) Russia, Canada, China, USA, Brazil and Australia.
(iii) Andaman and Nicobar group of islands.
(iv) Maldives, Sri Lanka.
3. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does this happen?
Answer
The longitudinal gap between Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat is about 30°. Due to this, there is time lag of about two hours between these states. Since Arunachal Pradesh is in the east hence the sun rises earlier here compared to in Gujarat. The Indian Standard Time is taken from the time of Standard Meridian of India and hence, the watches show the same time in both the states.
4. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
Answer
The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance because –
It has given India a strategic advantage due to the Trans Indian ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia.
The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean helps India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the Western coast and with the Southeast and East Asia from the Eastern coast.
The vast coastline and the natural harbours have benefitted India in carrying out trade and commerce with its neighbouring and distant countries.
It has given India a distinct climate than the rest of the Asian Continent.
Map Skills
1. Identify the following with the help of map reading.
(i) The island groups of India lying in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
(ii) The countries constituting Indian Subcontinent.
(iii) The states through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
(iv) The northernmost latitude in degrees.
(v) The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland in degrees.
(vi) The eastern and the western most longitudes in degrees.
(vii) The place situated on the three seas.
(viii)The strait separating Sri Lanka and India.
(ix) The Union Territories of India.
Answer
(i) Lakshadweep
(ii) Countries which make the Indian subcontinent are Pakistan in the north-west, India at the core, Nepal in the north, Bhutan in the north-east and Bangladesh in the east.
(iii) Tropic of Cancer passes through the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura and Mizoram.
(iv) 37°6′ N
(v) 8°4′ N
(vi) Western – 68°7′ E, Eastern – 97°25′ E
(vii) Kanyakumari
(viii) The Palk Strait.
(ix) Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Delhi, Lakshadweep, Puducherry (Pondicherry).